On February 17th, at the International Solid-State Circuits Conference (ISSCC) 2021, Professor Jun ZHOU's team from SICE made a presentation on their latest work titled "BioAIP: A Reconfigurable Biomedical AI Processor with Adaptive Learning for Versatile Intelligent Health Monitoring." This paper marks UESTC’sfirst ISSCC top conference paper in the field of AI chips. ISSCC is one of the most elite conferences in the chip domain, and their paper was accepted for ISSCC Processor Session, which had high participation from the industry. Other accepted papers came from renowned companies and universities such as Samsung, Hitachi, Renesas Electronics, MediaTek, and the University of California, Berkeley. UESTC was the sole institution associated with this paper. Doctoral student Jiahao LIU, guided by Professor Jun ZHOU, served as the first author, and Professor Jun ZHOU was the corresponding author. The chip design team comprised 12 members, and both frontend and backend design work were completed within the team.
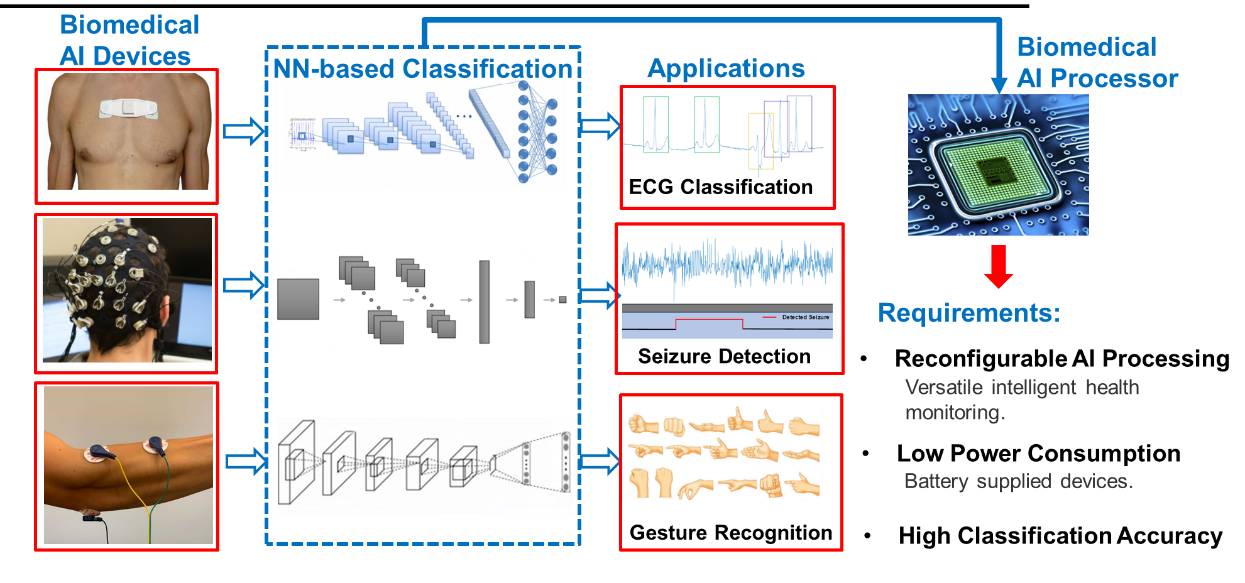
A core module for future wearable/implantable intelligent health monitoring devices is the AI processing chip for physiological signals. Existing general-purpose AI processing chips typically operate at the milliwatt level, making them unsuitable for ultra-low-power wearable/implantable health monitoring. Moreover, current physiological signal AI processing chips can only support a single AI health monitoring task (such as ECG recognition,epilepsydetection, motion sensing, emotion monitoring, etc.). Additionally, physiological signals may exhibit significant patient-to-patient variation, and pre-trained AI classification algorithms may experience a significant drop in accuracy for certain patients. To address these challenges, Professor Jun ZHOU's team developed an ultra-low-power, reconfigurable, and adaptive learning physiological signal AI processing chip called "BioAIP." In this chip, researchers designed a neural network processing engine with hardware reconfiguration capabilities that can perform calculations for different neural network structures, supporting various physiological signal AI processing algorithms. Simultaneously, they designed various flexibly configurable physiological signal processing engines, such as configurable filtering modules, peak detection modules, signal segmentation modules, etc., to support different physiological signal preprocessing tasks. The combination of these two aspects enables the chip to be used for various AI health monitoring applications. Based on this, the team proposed and implemented a series of ultra-low-power chip design technologies, including event-driven neural network processing architecture, on-chip data approximation compression technology, neural network/preprocessing engine reuse technology, adaptive physiological signal compression technology, etc. In multiple AI health monitoring tasks such as ECG recognition,epilepsydetection, and motion sensing, the chip achieved extremely low classification energy consumption of less than 6 microjoules. Additionally, considering the patient-to-patient variation in physiological signals, the research team proposed a low-complexity adaptive learning technology, allowing the AI algorithm to learn physiological signal characteristics for different patients, significantly improving accuracy without adding substantial power consumption. This AI processing chip can be used for various wearable/implantable intelligent health monitoring devices, offering broad application prospects.
In addition to this paper, Professor Jun ZHOU recently guided undergraduate students from Yingcai Honors CollegeofUESTC to publish work on neuromorphic processors in the top journal IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems – Part I (TCAS-I). Neuromorphic processors, also known as pulse neural network processors, are more similar to the real operation mechanism of the human brain compared to traditional AI chips. Neurons only emit pulses when activated and perform calculations only when pulses arrive, further reducing computational power consumption. Moreover, they possess a certain degree of unsupervised self-learning ability, making them a potential direction for the next generation of AI computing.
Professor Jun ZHOU's team primarily focuses on the design of AI-dedicated processing chips for intelligent perception terminals. They cater to applications such as image perception, wearable health monitoring, sound perception, electromagnetic perception, etc. Through collaborative chip and algorithm design, they aim to construct intelligent, low-power, miniaturized integrated solutions for intelligent perception. The team consists of 12 faculty members, including 5 professors/researchers (including 2 national young talents), 5 associate professors/researchers, and 2 lecturers/assistant researchers. They have led national key R&D programs, national natural science foundation joint key programs, national natural science foundation general programs, and other national projects. Additionally, they have collaborated with well-known companies such as SenseTime, Huawei, and BOE Technology in lateral cooperative projects. Joint labs have been established with leading AI enterprises like SenseTime and Intel. The research achievements have received accolades such as the IEEE Circuits and Systems Society Paper Award, China Invention and Innovation Award, China Industry-University-Research Cooperation Innovation Award, and Wu Wenjun Artificial Intelligence Technology Invention Award. In recent years, students guided by the team have won first prizes in national-level competitions such as the China Graduate Electronic Design Competition, China Graduate AI Innovation Competition, and the National College Student FPGA Innovation Design Competition.
Related Links:
ISSCC Paper Link: http://isscc.org/program-2
TCAS-I Paper Link: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9336327