Recently, Professor Kun QIU's optical communication research team from our university published a research paper in the internationally renowned journal "Light: Science and Applications." The paper is titled "Soliton bursts and deterministic dissipative Kerr soliton generation in auxiliary-assisted microcavities."
Doctoral student Yong GENG and Associate Professor Heng ZHOU are co-first authors of the paper, with UESTC as the first corresponding unit. Collaborating institutions include InstituteofFundamentalandFrontierSciences,UESTC, the University of California, Los Angeles, and the University of Colorado, Boulder. "Light: Science and Applications" is one of the top journals in the field of optics, with an impact factor of 13.6.
The integration of multi-wavelength light sources is crucial for wavelength-division multiplexing (WDM) optical communication systems. In recent years, the Kerr optical frequency comb technology based on optical microcavities has provided possibilities for achieving high-performance on-chip integrated WDM light sources. This technology has attracted significant attention from both the academic and industrial communities. Professor Kun QIU and Associate Professor Heng ZHOU's research group started studying Kerr optical comb technology in 2013 and has been dedicated to addressing key foundational issues in Kerr optical comb technology.
In this paper, the authors tackle the challenging problem of the susceptibility of Kerr optical combs to perturbations from optical microcavity thermal effects during the process of achieving dissipative soliton mode-locking. They propose an innovative technical solution called "auxiliary laser heating" to rationally regulate the thermal effects in the microcavity. This approach significantly expands the parameter range of dissipative solitons inside the microcavity, enhancing the flexibility, controllability, and stability of dissipative soliton mode-locking. This advancement greatly elevates the practical level of Kerr optical combs and lays the foundation for implementing soliton mode-locked Kerr optical combs in different material systems. Currently, the research team is collaborating with internationally renowned communication companies to explore new-generation communication light source technologies based on Kerr optical comb chips.
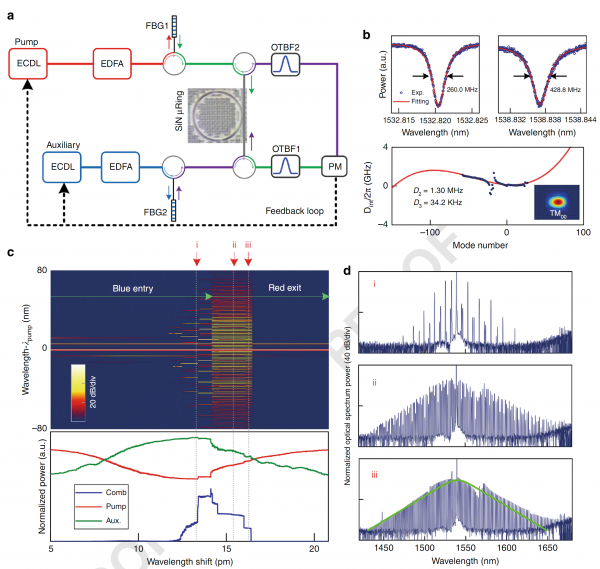
Caption: Schematic diagram of dissipative soliton mode-locking process in Kerr optical combs based on the auxiliary laser heating scheme
Professor Kun QIU's optical communication research team mainly focuses on fundamental and applied research in integrated photonics, optical transmission, and optical access. They have deep collaborations with well-known universities and enterprises both domestically and internationally, accumulating rich research achievements. The team has received a second-class National Technology Invention Award in 2015 and has published over 100 papers in journals such as "Light: Science and Applications," "Laser & Photonics Reviews," and "Physical Review Letters." They have led and completed major research projects funded by the Ministry of Science and Technology and the National Natural Science Foundation of China.
*Paper Link: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41377-019-0161-y